How big are tree roots
Understanding the Size of Tree Roots
When considering the growth and stability of trees, one essential aspect often overlooked is the significance of tree roots. While we may notice the majestic height and breadth of a tree, its root system plays an equally important role underground. In this article, we’ll explore the intricate world of roots and delve into the question of how big are tree roots? We will discuss root structures, the variability in sizes based on species, and their vital functions in tree health and stability.
The Anatomy of Tree Roots
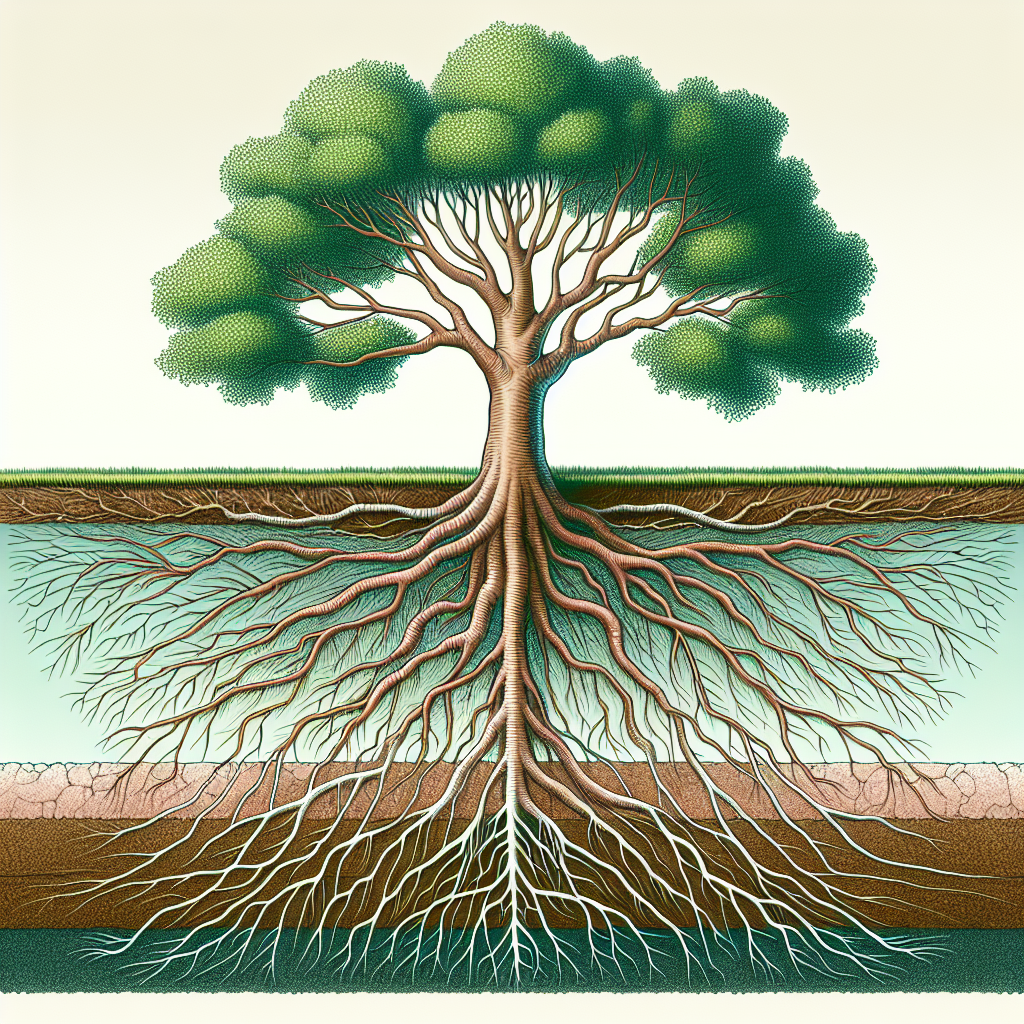
Roots are the hidden foundation of trees, anchoring them into the ground and supporting their growth. Understanding the anatomy of tree roots is crucial to appreciating their size and structure. Typically, a tree’s root system can be divided into three main parts:
- Taproots: A primary root that grows downward. It serves as an anchor and can store nutrients.
- Lateral Roots: These roots extend horizontally from the taproot, aiding in nutrient absorption and stability.
- Feeder Roots: These are finer roots that absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
How Tree Root Size Varies by Species
The size and depth of tree roots vary significantly depending on the species. Understanding this variability is key to answering the question of how big are tree roots in practical terms. Below are some examples of different trees and their general root characteristics:
- Oak Trees: They exhibit a robust root system with a deep taproot that can reach depths of 30 feet, while lateral roots can spread out 90 feet or more.
- Willow Trees: These trees often have shallow root systems that extend widely but do not go deep, typically only a few feet below the surface.
- Pine Trees: Depending on the species, pine roots can be extensive but often have a deep taproot that can reach 10 to 15 feet.
- Maple Trees: Maples generally have wide-spreading shallow roots that can extend beyond the canopy, typically around 30 feet across.
Factors That Influence Root Size
Understanding the various factors that influence root size provides insight into the differences observed among tree species. Some of the key factors include:
- Soil Type: Sandy soils allow for deeper root growth, while clay soils may restrict root expansion.
- Water Availability: Adequate water encourages root growth, while drought conditions can limit root development.
- Compaction: Soil compaction can inhibit the growth and spread of roots, leading to smaller root systems.
- Tree Age: Younger trees may have limited root systems, while mature trees typically develop extensive networks.
Soil Type and Its Impact
Different soils provide different levels of resistance and nutrient availability. For instance:
| Soil Type | Root Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Sandy | Allows deep penetration; promotes extensive root systems. |
| Clay | Restricts root spread; roots tend to stay near the surface. |
| Loamy | Balanced in texture; supports robust root growth. |
Water Availability
Water availability plays a fundamental role in root development. Trees under drought stress tend to develop:
- Shallower root systems
- More extensive lateral roots in search of moisture
- Reduced overall growth
Importance of Understanding Tree Roots
The understanding of tree roots extends beyond their size and structure; it influences many aspects of tree care, landscaping, and environmental health. Let's look at some critical reasons why grasping the concept of tree roots is important:
- Stability: A tree’s stability is often determined by the strength and spread of its root system.
- Water and Nutrient Absorption: Larger root systems can access more water and nutrients, contributing to healthier trees.
- Soil Erosion Prevention: Extensive roots help hold the soil together, reducing the risk of erosion.
- Tree Health: Understanding root vitality can help in diagnosing and treating tree health issues.
The Role of Tree Roots in Ecosystem Health
Tree roots don't just contribute to the individual plant's health; they play a vital role in the ecosystem. They assist in:
- Carbon Sequestration: Trees absorb carbon dioxide, and strong roots help stabilize and promote healthy tree growth for this purpose.
- Biodiversity: Root systems provide habitats for various organisms, aiding in biodiversity.
- Soil Health: Roots interact with microorganisms in the soil, enhancing nutrient cycling and improving soil structure.
Conclusion: The Hidden Giants Beneath Us
In exploring the question of how big are tree roots, we uncover a fascinating interplay of factors that contribute to their growth and size. From the type of soil to the species of tree, the underground labyrinth of roots tells a story of stability, sustainability, and ecological significance. As we cultivate and preserve our green spaces, it becomes increasingly important to recognize not only the trees we see but also the hidden giants beneath our feet that support the life above. Understanding tree roots provides crucial insights not only for horticulturists and arborists but also for homeowners, city planners, and anyone invested in maintaining a healthy environment.
"The roots of a tree reach deep into the earth, reminding us of the strength derived from what lies beneath." – Anonymous``` This article includes the appropriate HTML structure and necessary content related to the topic of tree roots while ensuring the keyword "how big are tree roots" appears only three times.
By Guest, Published on August 7th, 2024