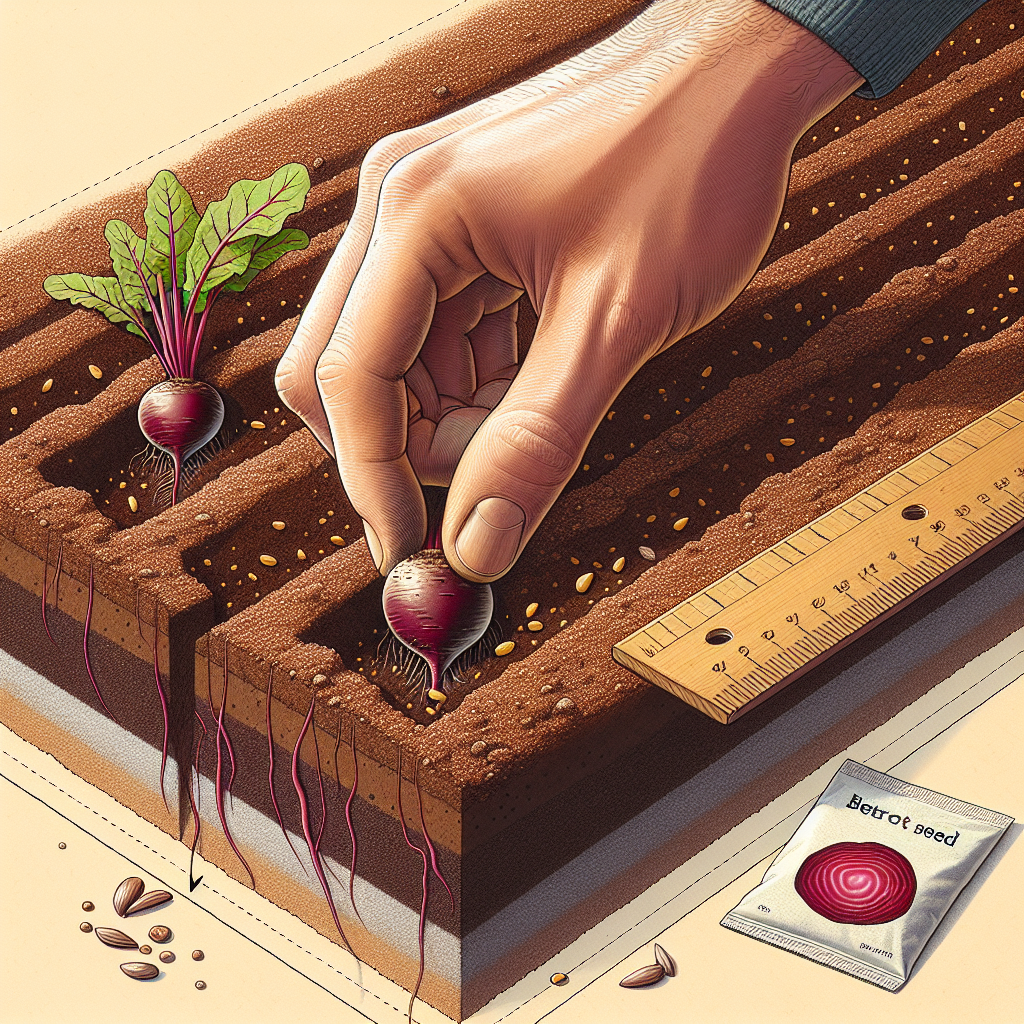
How deep to plant beetroot seeds
Growing Beetroot: A Beginner's Guide
Beetroot, with its vibrant color and earthy flavor, is a favorite among gardeners and cooks alike. Not only is it nutritious, but it's also quite enjoyable to grow. If you’re new to gardening or just want to ensure the best results, understanding how deep to plant beetroot seeds is crucial. In this article, we will guide you through the process, tips, and tricks for successfully cultivating beetroot in your garden.
Why Grow Beetroot?
Beetroot, also known simply as beets, is rich in nutrients, loaded with vitamins, and offers a plethora of culinary possibilities. Besides providing an excellent source of dietary fiber, folate, and antioxidant compounds, beets can also improve cardiovascular health and lower blood pressure.
Here are some other reasons to consider growing your own beetroot:
- Versatility: Beets can be roasted, boiled, or pickled, and their greens are edible too.
- Easy to Grow: They are relatively low-maintenance, making them perfect for beginner gardeners.
- Attractive Plants: With their colorful roots and lush foliage, beets can add visual interest to your garden.
The Best Time to Plant Beetroot Seeds
Timing is crucial when planting beetroot seeds. They thrive in cooler weather, making them ideal for spring and fall planting. In most climates, you can seed beetroot from March to July, ensuring you dodge the summer heat that can hinder their growth.
Here are some tips for optimal planting times:
- In cooler climates, plant early spring for a summer harvest.
- For fall crops, sow seeds in late summer.
- Always check your local frost dates to avoid late frosts that can damage seedlings.
How Deep to Plant Beetroot Seeds?
When it comes to planting beetroot seeds, **how deep to plant beetroot seeds** is a common question among new gardeners. The ideal depth for planting is about 1 inch (2.5 cm) deep. This depth is sufficient for the seeds to germinate while ensuring they are not too close to the soil surface, which can expose them to birds and other pests.
It’s essential to give beetroot seeds enough room to develop their impressive roots, so proper spacing is equally crucial. Here are some additional considerations:
- Space seeds about 3 inches apart to give them ample room to grow.
- If you’re planting multiple rows, keep rows about 12 inches apart for easy access and maintenance.
Preparing Your Garden Bed
Before planting beetroot seeds, preparing your garden bed is essential for healthy growth. Here’s how to set the stage for success:
- Select a Location: Choose a spot with full sun for at least 6 hours a day.
- Soil Quality: Aim for well-drained, loamy soil enriched with organic matter.
- pH Level: Beetroot prefers a slightly acidic to neutral pH (6.0 to 7.0).
- Soil Preparation: Clear weeds and debris, then till the soil to a depth of at least 12 inches. Mix in compost or rotted manure to enhance soil fertility.
Planting Beetroot Seeds
Once your garden bed is prepared, you can start planting your beetroot seeds. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Make shallow furrows in the soil, about 1 inch deep, following the planned spacing.
- Drop seeds into the furrows, ideally 2-3 seeds per spot.
- Cover the seeds gently with soil and pat down lightly to ensure good soil contact.
- Water the area lightly using a fine spray to avoid disturbing the seeds.
Watering and Fertilizing
After planting beetroot seeds, maintaining moisture is vital for germination. Here are some tips on watering and fertilization:
- Initial Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist until seeds germinate, which typically takes about 5-10 days.
- Regular Watering: Once seedlings emerge, water them regularly, about 1 inch per week, ensuring deep roots.
- Fertilization: Use a balanced fertilizer when plants are 3-4 inches tall for optimal growth.
Weeding and Mulching
Keeping your beetroot patch weed-free will help ensure a healthy crop. Weeds compete for nutrients and water, so regular maintenance is necessary:
- Hand Weeding: Remove weeds by hand or with a hoe, being careful not to disturb beetroot roots.
- Mulching: Consider organic mulch materials like straw or grass clippings, which can suppress weeds and retain moisture.
Pest and Disease Management
Beetroot can be susceptible to various pests and diseases. Being proactive can help you avoid significant issues:
- Pests: Watch out for aphids, leaf miners, and beetles. Introduce beneficial insects or consider insecticidal soap.
- Diseases: Prevent fungal infections by ensuring good air circulation and avoiding overhead watering.
Harvesting Beetroot
Timing your harvest is key to enjoying delicious beetroot. Here’s what you need to know:
- Harvest Time: Beetroots can be harvested whenever they reach an appropriate size, typically between 2-3 months after planting.
- Checking Size: Gently dig around the root to check size; young beetroots are sweeter and tenderer.
- Technique: Be sure to twist rather than pull to avoid breaking the roots.
Storing and Preserving Beetroot
Once you've harvested your beetroot, proper storage is key to maintaining its quality:
- Cleaning: Remove stems and roots; do not wash until ready to use.
- Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, dark place, ideally at temperatures around 32°F to 40°F (0°C to 4°C).
- Preservation Methods: Consider pickling or roasting beetroot for long-term storage.
Conclusion
Growing beetroot can be a rewarding and enjoyable endeavor. Understanding the best practices for planting, including how deep to plant beetroot seeds, among other necessary care details, will lead you to delicious results. Whether you choose to eat them fresh, roast them in a dish, or pickle them for later, your garden-grown beets are sure to impress.
Now that you have the knowledge in hand, it’s time to roll up your sleeves and get planting!
``` This article provides comprehensive insights on planting and cultivating beetroot while strategically integrating the target keyword, ensuring it doesn’t exceed the specified limit.By Guest, Published on October 1st, 2024