How do you get rose seeds
How to Cultivate Your Own Rose Seeds: A Comprehensive Guide
With their vibrant colors and delightful fragrances, roses are a favorite among gardeners and flower enthusiasts. While most people purchase rose bushes at nurseries or garden centers, growing roses from seeds can be a rewarding and fascinating experience. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of acquiring and germinating rose seeds, helping you blossom into a successful rose grower.
Understanding Rose Seeds
Before you dive into the fascinating world of rose seed cultivation, it’s crucial to understand what rose seeds are and where they come from. Rose seeds develop from the rose hips, which are the fruit of the rose plant. These hips form after the flowers have been pollinated and have typically matured from late summer to early fall.
Not all roses produce seeds, and not all seeds yield the same quality or type of rose. The characteristics of the seedlings can vary greatly, even if they come from the same parent plants. So, if you’re asking yourself how do you get rose seeds, the answer largely depends on finding healthy rose hips and understanding the process of seed extraction.
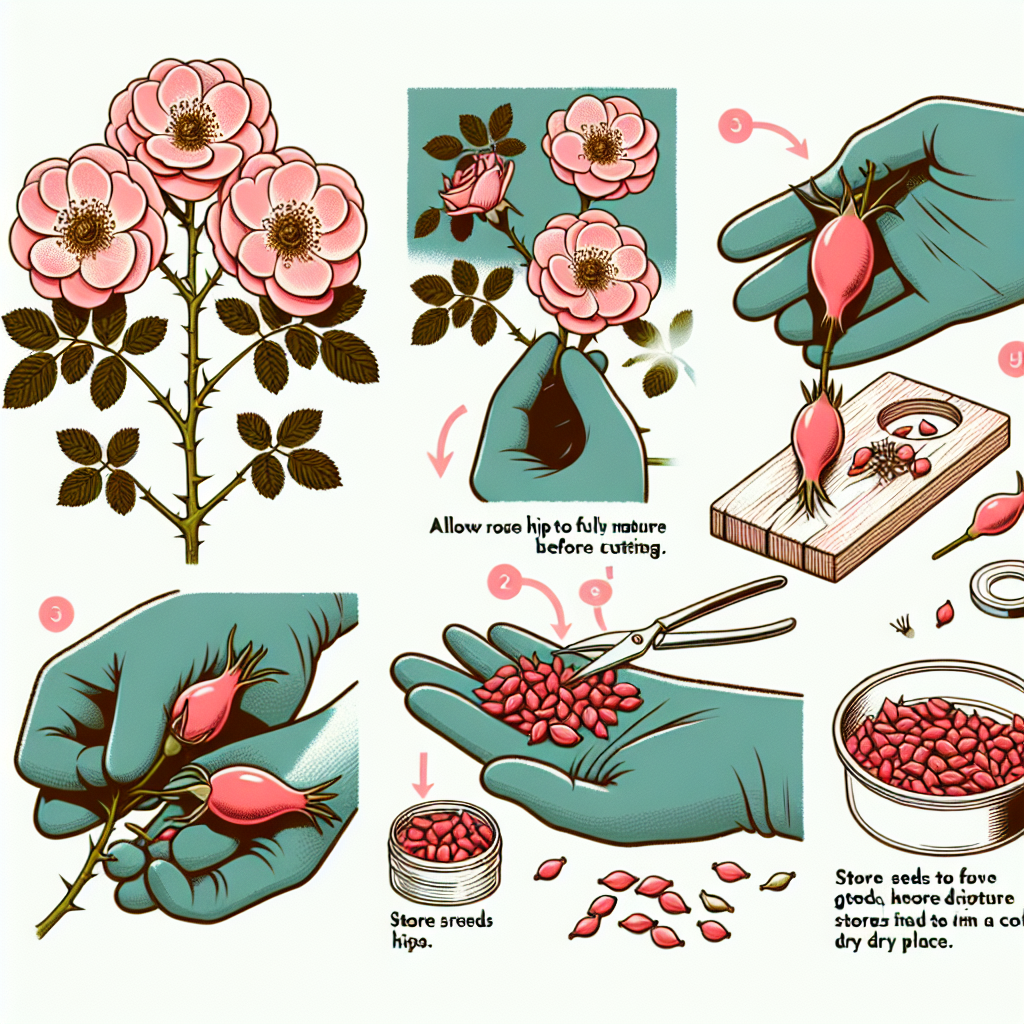
How to Collect Rose Seeds
Collecting rose seeds may seem daunting, but it’s quite simple with the right approach. Follow these steps to ensure you gather viable seeds:
- Choose Healthy Roses: Look for vigorous roses in your garden or local area. Ideally, select ones that are disease-resistant and known for their beautiful blooms.
- Wait for the Hips to Mature: After the blooms have faded, the petals will drop, and rose hips will begin to form. Allow these hips to ripen fully; this usually takes several weeks.
- Harvest the Hips: Once the hips are red, orange, or deep purple and ripe, harvest them by cutting them off the stem with a pair of pruning shears.
- Extract the Seeds: Cut the hips open carefully and remove the seeds. There may be several seeds in each hip. Rinse the seeds to remove any surrounding pulp, which can inhibit germination.
Preparing Rose Seeds for Germination
Once you have collected and cleaned your rose seeds, preparing them for germination is the next crucial step. Most rose seeds require a process known as stratification to break their dormancy. Here’s how to do it:
- Moist Cold Stratification: Place the seeds in a moist paper towel and then into a plastic bag. Seal the bag and refrigerate it for about 6-10 weeks. This mimics the seeds' natural winter environment, preparing them for germination.
- Check Regularly: Every week, check the seeds to ensure they remain moist. If the towel dries out, spray it lightly with water.
- Prepare for Planting: After the cold stratification period, you’re ready to plant your seeds. Use a sterile potting mix for best results.
Germinating Rose Seeds
Now that your seeds have been prepared, it’s time to germinate them. Follow these steps for successful germination:
- Filling Containers: Fill small pots or seed trays with moistened potting mix. Leave space at the top to accommodate watering.
- Planting the Seeds: Plant the seeds about 1/4 inch deep in the soil. Cover them lightly with soil and gently press down to eliminate any air pockets.
- Watering: Water the planted seeds carefully, ensuring the soil is moist but not soggy. The moisture level is crucial for seed germination.
- Creating the Right Environment: Cover the pots with plastic wrap or a clear dome to create a greenhouse effect, which helps retain humidity. Place the pots in a warm area with indirect sunlight.
After Germination Care
Once the seeds begin to sprout, typically within 2-3 weeks, it’s essential to provide them with the right care to ensure healthy growth:
- Removing the Cover: Once the seedlings have developed their first set of true leaves, remove the plastic cover gradually to prevent shock.
- Transplanting: When the seedlings are around 2-3 inches tall and have developed several leaves, transplant them into larger pots, ensuring they have plenty of space to grow.
- Fertilizing: Start with a diluted, balanced fertilizer every 4-6 weeks to provide essential nutrients as they grow.
- Sunlight Exposure: Ensure that the seedlings receive plenty of bright, indirect sunlight. Avoid direct harsh sunlight until they are well established.
Transplanting Your Rose Seedlings
As your seedlings grow, they will eventually need to be transplanted into the garden or larger pots. Follow these steps to ensure a successful transition:
- Choosing the Right Time: Transplant your seedlings outdoors in the spring after the last frost date, when they are about 6-8 inches tall and have developed a strong root system.
- Preparing the Site: Select a sunny location with well-draining soil. Amend the soil with organic compost to provide essential nutrients.
- Transplanting: Carefully dig a hole larger than the root ball, and place the seedling in the hole at the same depth it was in the pot. Backfill the hole with soil and firm it gently.
- Watering: Water thoroughly after transplanting, and keep the soil consistently moist until the plants establish themselves.
Maintaining Your Roses
Once your roses are in the ground, it’s vital to maintain them properly to encourage vigorous growth and beautiful blooms. Keep the following points in mind:
- Regular Watering: Ensure your roses receive a deep watering at least once a week, especially during dry spells.
- Pruning: Prune your roses at the right time each season to promote new growth and flowering. Remove dead or diseased canes and shape the plant for optimal sunlight exposure.
- Pest and Disease Control: Monitor your roses regularly for pests and diseases. Employ organic treatments when possible to protect the environment and beneficial insects.
Conclusion: Your Rose-Growing Journey
Growing roses from seeds may take time and patience, but the results can be incredibly rewarding. Not only do you get to enjoy the beauty of your blooms, but you also gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate biology of these beloved plants. Remember, whether you’re just starting out or you’re a seasoned gardener, understanding how do you get rose seeds and nurturing them through the planting, germination, and growth stages will pave the way for your own picturesque rose garden. Happy gardening!
“To plant a garden is to believe in tomorrow.” – Audrey Hepburn
By Guest, Published on September 20th, 2024