How to grow cucumber in a raised bed
How to Grow Cucumber in a Raised Bed: A Comprehensive Guide
Growing cucumber in a raised bed offers numerous advantages, including improved soil drainage, ease of access, and better control over soil quality. If you are looking to cultivate healthy and delicious cucumbers, this guide will provide you with all the necessary information you need.
Why Choose Raised Beds for Cucumber Cultivation?
Raised beds are an excellent option for growing cucumbers for several reasons:
- Soil Quality: Raised beds can be filled with high-quality soil tailored specifically for cucumbers, ensuring optimal growth conditions.
- Drainage: Improved drainage prevents waterlogging, which is crucial for healthy cucumber plants that thrive in moist but well-drained soils.
- Accessibility: Heightened beds make it easier to tend and harvest without bending over excessively, reducing strain on your back.
- Pest Control: Elevating plants can help deter certain ground-based pests.
Choosing the Right Location
When setting up your raised bed for growing cucumber, location matters significantly. Here are some tips:
- Sunlight Exposure: Select a spot that receives at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily, as cucumbers are sunlight-loving plants.
- Air Circulation: Ensure the area has good air circulation to reduce the risk of diseases.
- Accessibility: Choose a location that’s easy to access for maintenance and harvesting.
Preparing Your Raised Bed
Before planting cucumbers, it’s important to prepare your raised bed properly. Here’s how:
- Size: A raised bed should ideally be at least 4 feet wide and 6-8 feet long for optimum growing space.
- Soil Mix: Fill the bed with a nutrient-rich soil mix consisting of topsoil, compost, and organic amendments like peat moss. Ideal soil pH for cucumbers is around 6.0 to 6.8.
- Fertilization: Incorporate a balanced fertilizer into the top 6 inches of soil to provide essential nutrients for your plants.
Choosing Cucumber Varieties
There are several cucumber varieties to choose from, each with its unique characteristics. Some popular varieties include:
- Slicing Cucumbers: These are typically larger, perfect for fresh salads. Example: 'Marketmore 76'.
- Pickling Cucumbers: Smaller and bumpier, ideal for preservation. Example: 'National Pickling'.
- Burpless Cucumbers: These varieties are easier to digest and are often sweeter. Example: 'Sweet Success'.
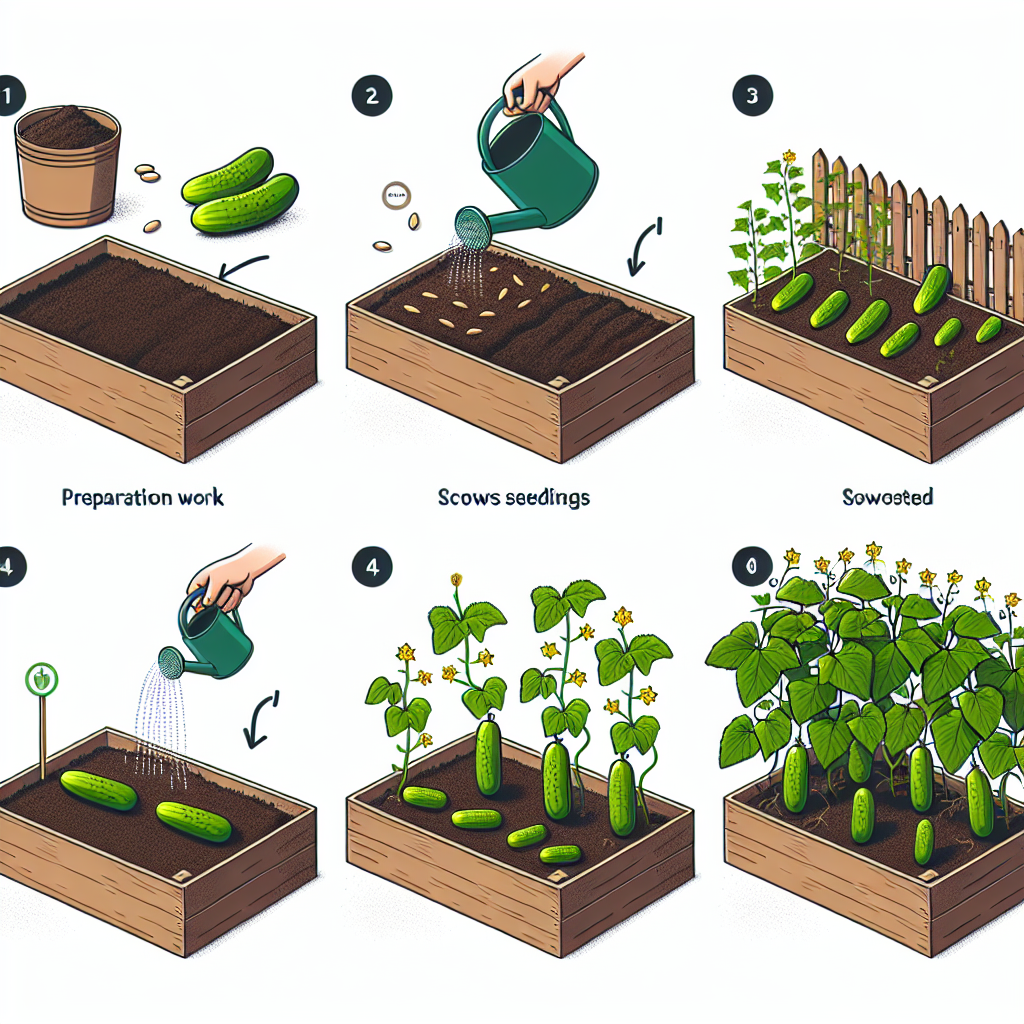
Planting Cucumbers in a Raised Bed
Once your bed is ready and you have chosen the right cucumber variety, it’s time to plant. Follow these steps:
- Planting Time: Wait until the danger of frost has passed and soil temperatures reach at least 70°F (21°C).
- Sow Seeds or Transplant: If sowing seeds, plant them about 1 inch deep, spaced 12 inches apart in rows. If transplanting seedlings, be careful not to disturb the roots.
- Watering: Water thoroughly after planting. Consistent moisture is vital, especially during germination and early growth stages.
Support and Training
Cucumbers can grow sprawling vines, so providing support can help promote healthy growth and easier harvesting. Here are some methods:
- Trellising: Use a trellis or cage to allow cucumbers to grow vertically, saving space in your raised bed.
- Fencing: Use a sturdy fence that cucumbers can cling to while they grow.
- Stakes: If using stakes, make sure they are tall enough (at least 4-6 feet) to support the mature plants.
Ongoing Care: Watering, Fertilization, and Pest Management
To ensure your cucumbers thrive, continuous care is essential. Pay attention to the following aspects:
Watering
Cucumbers require consistent moisture to grow well:
- Water deeply once or twice a week, depending on weather conditions.
- Avoid wetting the foliage to reduce disease risks.
- Mulching with straw or wood chips can help retain soil moisture.
Fertilization
As your cucumbers grow, they may benefit from additional nutrients:
- Feed: Use a balanced fertilizer every few weeks once flowers begin to appear.
- Organic Options: Compost tea or fish emulsion works well too.
Pest Management
Being proactive about pest control can save your cucumber crop:
- Regular Checks: Inspect leaves for signs of pests like aphids, cucumber beetles, and spider mites.
- Biological Control: Introduce beneficial insects, such as ladybugs to control pest populations naturally.
- Companion Planting: Plant marigolds or other flowers that attract beneficial insects near your cucumber bed.
Harvesting Cucumbers
Knowing when and how to harvest your cucumbers is crucial for the best flavor:
- Harvest Time: Typically, cucumbers are ready to harvest 50-70 days after planting, depending on the variety.
- Size: For slicing cucumbers, harvest when they are about 6-8 inches long; pickling cucumbers can be harvested smaller, around 4-6 inches.
- Method: Use scissors or pruning shears to avoid damaging the plant, and harvest regularly to encourage more fruit production.
Common Issues and Solutions
Even with proper care, you may encounter some common problems when growing cucumbers in a raised bed:
| Issue | Symptoms | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Powdery Mildew | White powdery spots on leaves | Improve air circulation, use a fungicide if necessary. |
| Blossom End Rot | Dark, sunken spots on fruit | Ensure consistent watering and adequate calcium. |
| Cucumber Beetles | Chewed leaves and wilting | Handpick them or use insecticidal soap. |
Conclusion
When it comes to how to grow cucumber in a raised bed, following these guidelines can lead to a bountiful harvest. By providing the right environment, monitoring plant health, and addressing issues promptly, you will enjoy the fruits of your labor. Get ready to relish fresh, crunchy cucumbers straight from your garden!
By Guest, Published on August 25th, 2024