How to grow rose plant from flower
How to Grow Rose Plant from Flower: A Comprehensive Guide
Rose plants are beloved for their stunning blooms and delightful fragrances. The notion of propagating a rose plant from a flower may seem daunting, but it's a rewarding process that can yield impressive results. This guide will cover the essential steps and techniques needed to successfully grow a rose plant from a flower, ensuring you can enjoy beautiful roses in your garden or home.
Understanding Rose Propagation
Before diving into the methods of how to grow rose plant from flower, it's important to understand the basics of rose propagation. Propagation is the process of creating new plants from existing ones. While many gardeners are familiar with propagation through cuttings, growing roses from a flower involves a slightly different approach.
Choosing the Right Flower
To start the process, select a healthy and vibrant rose flower. It's crucial to keep in mind the following considerations when making your selection:
- Choose Fresh Flowers: Opt for flowers that are still in bloom and have vivid colors.
- Variety Matters: Some rose varieties are more suitable for propagation than others. Look for varieties known for their resilient nature.
- Time of Year: Spring and early summer are usually the best times to cut flowers for propagation, as roses are in their active growth phase during these seasons.
Gathering Necessary Supplies
Before you begin the process of propagating a rose plant, it's important to gather the necessary supplies. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Sharp sterilized pruning shears
- A clean vial or container of water
- Rooting hormone (optional, but helpful)
- Small pots or trays filled with potting soil
- Plastic bags or a humidity dome
Steps to Grow a Rose Plant from a Flower
Now that you have everything ready, let’s delve into the step-by-step process of how to grow rose plant from flower.
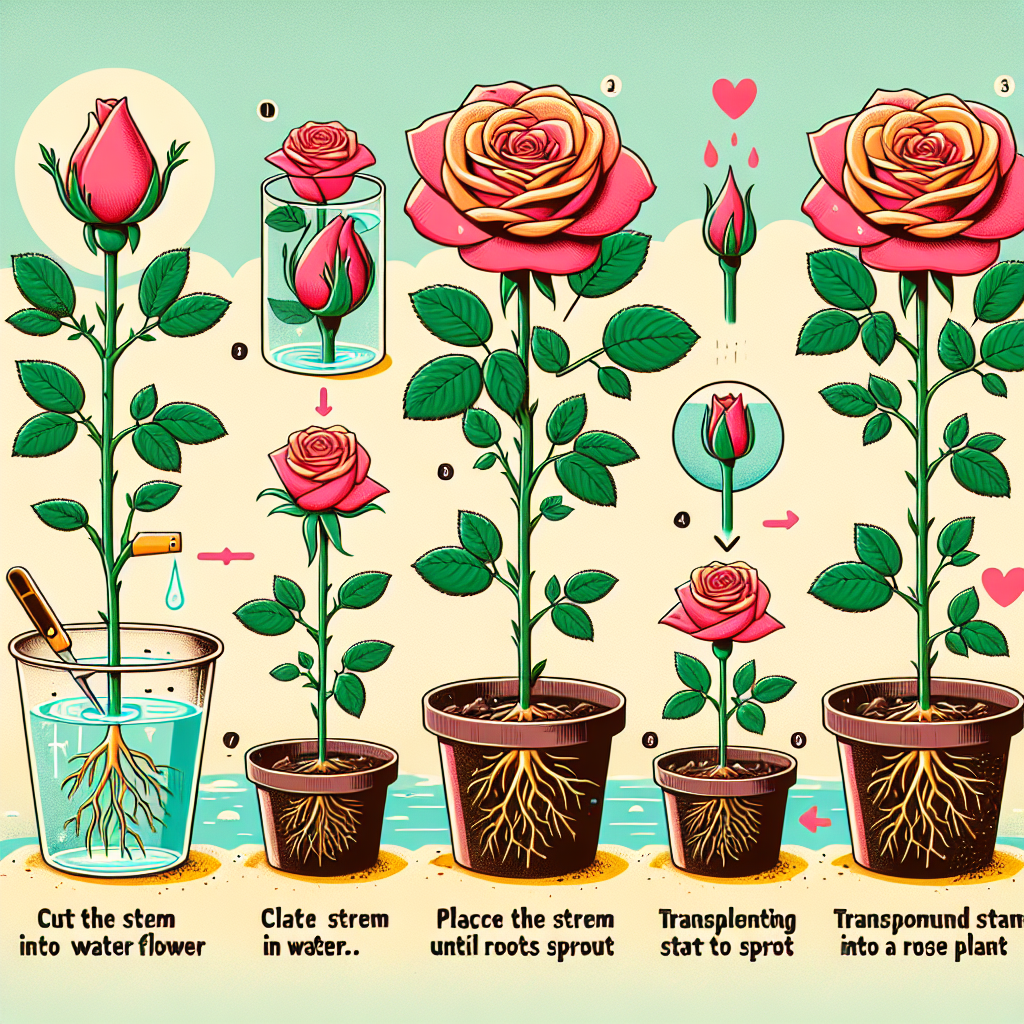
Step 1: Cut the Flower
Using the sterilized pruning shears, carefully snip a healthy rose flower from the plant. Ensure that you make a clean cut just below the bloom to capture some stem length.
Step 2: Prepare the Stem
Remove any leaves from the lower part of the stem, leaving only a couple of leaves at the top. This helps redirect the plant's energy towards root development. If you wish, you can dip the cut end into rooting hormone to enhance root production.
Step 3: Place in Water
Next, place the cut flower in a clean vial or container of water. Ensure that the cut end is submerged while the leaves remain above water. This method allows the stem to absorb moisture as it begins to develop roots.
Step 4: Monitor and Change Water
Keep the container in a bright but indirect sunlight area. It's essential to change the water every few days to ensure that it remains fresh and oxygenated. In about 1 to 3 weeks, you should start to see roots forming.
Step 5: Transplanting to Soil
Once the roots are approximately 2 inches long, it’s time to transplant the cutting into potting soil. Follow these steps for a successful transplant:
- Prepare a small pot with well-draining potting soil.
- Create a small hole in the soil using your finger or a pencil.
- Gently place the rooted cutting in the hole and cover it with soil.
- Water the soil lightly to help settle it around the roots.
Creating the Right Environment
After transplanting, it's vital to create an optimal environment for your new rose plant. Here are some tips to consider:
- Humidity: To maintain humidity, cover the pot with a plastic bag or use a humidity dome. This creates a greenhouse effect that helps the plant acclimatize.
- Light: Place the pot in a location that receives bright but indirect sunlight. Avoid direct sunlight until the plant is established.
- Watering: Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. Too much water can lead to root rot, while too little can hinder growth.
Patience and Care
As your rose cutting begins to grow, it is essential to provide ongoing care. Monitor the plant's progress, and within a few weeks or months, you should begin to see new growth. During this time, it’s important to:
- Gradually remove the humidity cover as the plant becomes established.
- Begin fertilizing with a balanced fertilizer as new leaves emerge.
- Prune any dead or unhealthy leaves to encourage growth.
Transplanting Outdoors
Once your rose plant is established and has outgrown its pot, you may wish to transplant it into the garden. Timing is key; wait until all danger of frost has passed. Here’s how to properly transplant your rose:
- Choose a location with well-draining soil and at least 6 hours of sunlight per day.
- Dig a hole that is about twice the size of the plant’s root ball.
- Carefully remove the plant from its pot and place it in the hole.
- Cover the roots with soil and water thoroughly.
Common Challenges When Growing Roses
While growing roses can be a delightful experience, it’s not without its challenges. Here are some common issues to be aware of:
- Pests: Aphids and spider mites can be detrimental to rose plants. Regular checks and organic pest control methods can help.
- Diseases: Fungal infections, such as black spot, can affect roses. Ensure good air circulation and proper spacing of plants.
- Improper Watering: Both overwatering and underwatering can hinder growth. Always check the soil moisture before watering.
Conclusion
Understanding how to grow rose plant from flower is a fulfilling journey that aids in creating your beautiful garden. From selecting the right flower to nurturing your new plant, each step is crucial for success. With patience, care, and attention to detail, you can propagate roses that not only bloom beautifully but also bring joy and fragrance to your life.
Give it a try, and soon, you may find yourself surrounded by lush roses that you cultivated right from a single flower!
By Guest, Published on August 27th, 2024