How to grow spinach at home
How to Grow Spinach at Home: A Comprehensive Guide
If you’re looking to add some fresh, nutritious greens to your diet, learning how to grow spinach at home is an excellent start. Spinach is not only versatile in the kitchen but also a powerhouse of vitamins and minerals. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essentials of cultivating spinach, from choosing the right variety to harvesting. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or just starting, you’ll find all the tips you need to successfully grow spinach in your own backyard or balcony.
Why Grow Spinach?
- Nutritional Benefits: Spinach is rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as iron and calcium. It's a great addition to a healthy diet.
- Quick Growth: Spinach is a fast-growing crop, typically maturing within 6 to 8 weeks.
- Space-Efficient: You can grow spinach in small spaces, making it ideal for urban gardening or container gardening.
- Continuous Harvesting: If you practice proper harvesting techniques, you can enjoy spinach throughout the growing season.
Choosing the Right Spinach Variety
Before you dive into how to grow spinach at home, it’s important to select the right variety for your climate and growing conditions. Here are a few common types:
- Savoy Spinach: Known for its crinkly leaves and robust flavor, it's often used in salads and cooking.
- Flat-Leaf Spinach: This variety has smooth, broad leaves and is popular for canning and freezing.
- Baby Spinach: Harvested at an earlier stage, baby spinach has tender leaves and is perfect for salads.
When to Plant Spinach
Timing is crucial for successful spinach cultivation. Here are the best times to plant:
- Spring Planting: Spinach can be planted as soon as the soil can be worked, typically 2-4 weeks before the last frost.
- Fall Planting: In mild climates, spinach can also be planted in late summer or early fall for a winter crop.
Preparing the Soil
Healthy soil is the foundation for growing spinach. Here’s how to prepare your soil:
- Soil Testing: Conduct a soil test to determine pH and nutrient levels. Spinach prefers a slightly acidic to neutral pH of 6.0 to 7.0.
- Amending Soil: Incorporate well-rotted compost or aged manure to enrich the soil with nutrients and improve drainage.
- Tilling: Loosen the soil to a depth of about 12 inches to facilitate root growth.
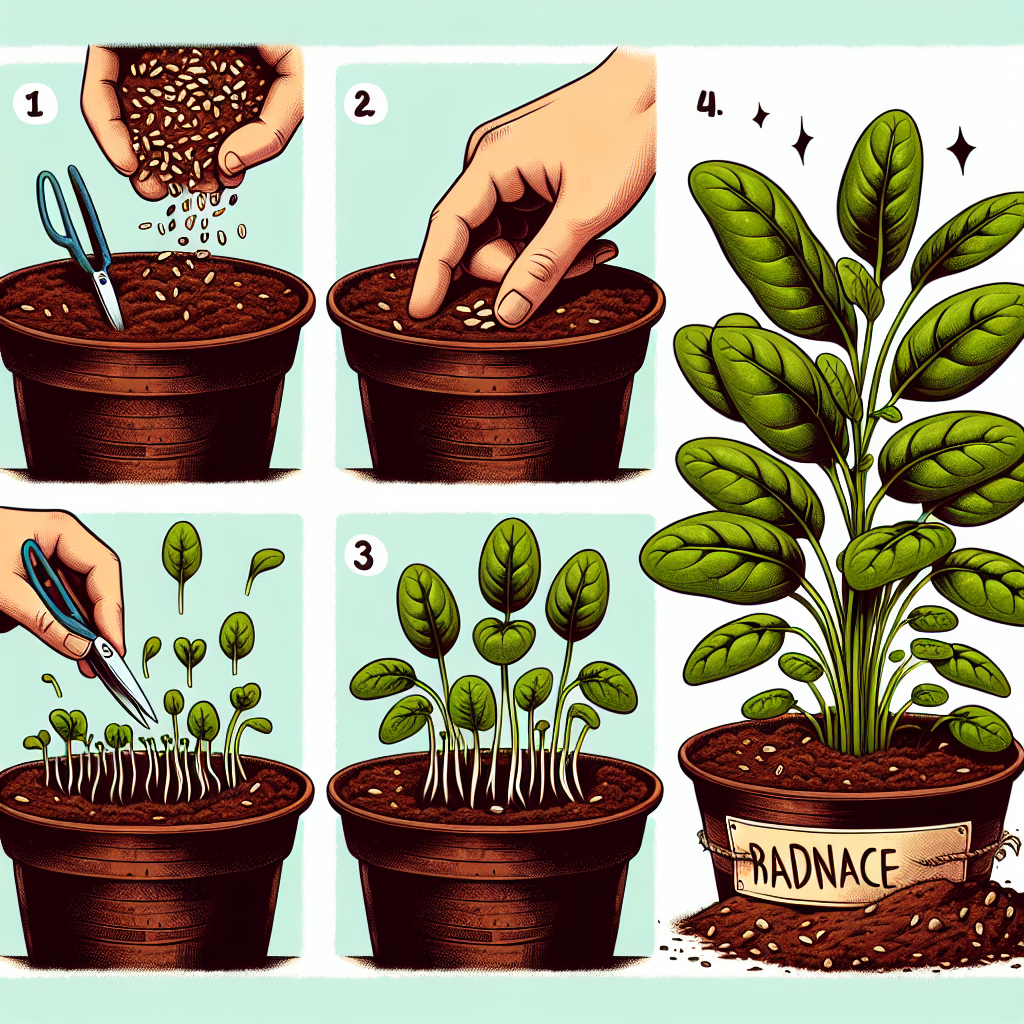
Planting Spinach Seeds
Once your soil is ready, it's time to plant your seeds. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Seed Depth: Plant seeds about ½ to 1 inch deep.
- Spacing: Space the seeds 2 inches apart in rows that are 12 to 18 inches apart.
- Thinning: Once seedlings are about 2 inches tall, thin them out to ensure that they have enough room to grow.
Watering and Fertilizing
Spinach requires consistent moisture and nutrient support to thrive.
- Watering: Keep the soil evenly moist, especially during dry spells. Water deep and less frequently to encourage deep root growth.
- Fertilizing: Apply a balanced fertilizer or compost every 4 to 6 weeks to provide the necessary nutrients for growth.
Pest and Disease Management
As you learn how to grow spinach at home, it's crucial to be aware of potential pests and diseases:
- Common Pests: Aphids, leaf miners, and slugs can be problematic. Consider using row covers to protect young plants.
- Diseases: Watch out for downy mildew and powdery mildew. Ensure proper spacing and air circulation to minimize the risk.
Harvesting Spinach
Knowing when and how to harvest your spinach is essential for getting the most out of your crop:
- Timing: Begin harvesting when leaves are young and tender, typically 6 to 8 weeks after planting.
- Technique: Use scissors to snip off the outer leaves, allowing the inner leaves to continue growing. This method encourages continuous production.
- Storage: Freshly harvested spinach can be stored in the refrigerator for up to a week. For longer storage, consider blanching and freezing the leaves.
Continuous Production for a Year-Round Harvest
For gardeners looking for extended harvests, consider the following tips:
- Succession Planting: Plant a new batch of seeds every 2-3 weeks to ensure a continuous supply of fresh spinach.
- Season Extension: Use hoops and plastic covers to protect plants from frost during fall and winter or consider growing spinach indoors.
- Companion Planting: Plant spinach alongside other crops, such as radishes and lettuce, to maximize your garden space.'}
Conclusion
Growing spinach at home can be a highly rewarding experience. With its nutritional benefits and adaptability to various growing conditions, spinach is an excellent choice for anyone interested in gardening. Follow these guidelines on how to grow spinach at home, and you’ll be well on your way to enjoying fresh spinach in your salads, smoothies, and more. Happy gardening!
By Guest, Published on October 5th, 2024