How to grow strawberries from a strawberry
How to Grow Strawberries from a Strawberry: A Complete Guide
Growing your own strawberries can be a rewarding experience that not only brings sweet and juicy fruit to your table but also enhances your gardening skills. Many people are surprised to learn that you can actually grow strawberries from the fruit itself. This article will guide you on how to grow strawberries from a strawberry and provide useful tips for successful cultivation.
Understanding Strawberries
Strawberries belong to the genus *Fragaria*, which includes several species, most commonly *Fragaria × ananassa*, the garden strawberry. These delicious fruits are not only versatile in the kitchen but also packed with vitamins and antioxidants. Growing strawberries at home allows you to enjoy them fresh and free from pesticides.
The Right Time for Planting Strawberries
While strawberries can be grown from seeds, propagating them directly from the fruit is an interesting process. The best time to start depends on your local climate, but generally, late winter to early spring is ideal for planting. Here’s a breakdown:
- Winter (January - February): Start preparing your seeds indoors.
- Spring (March - April): Time to grow them outdoors after the last frost.
- Summer (June - July): Keep tending to your plants and harvest time!
Getting Started: What You Need
Before diving into the planting process, ensure you have the right materials ready for a successful venture. Here’s a checklist:
- A ripe strawberry
- A container with good drainage
- Potting soil or seed starting mix
- Watering can or spray bottle
- Plastic wrap or a clear plastic bag
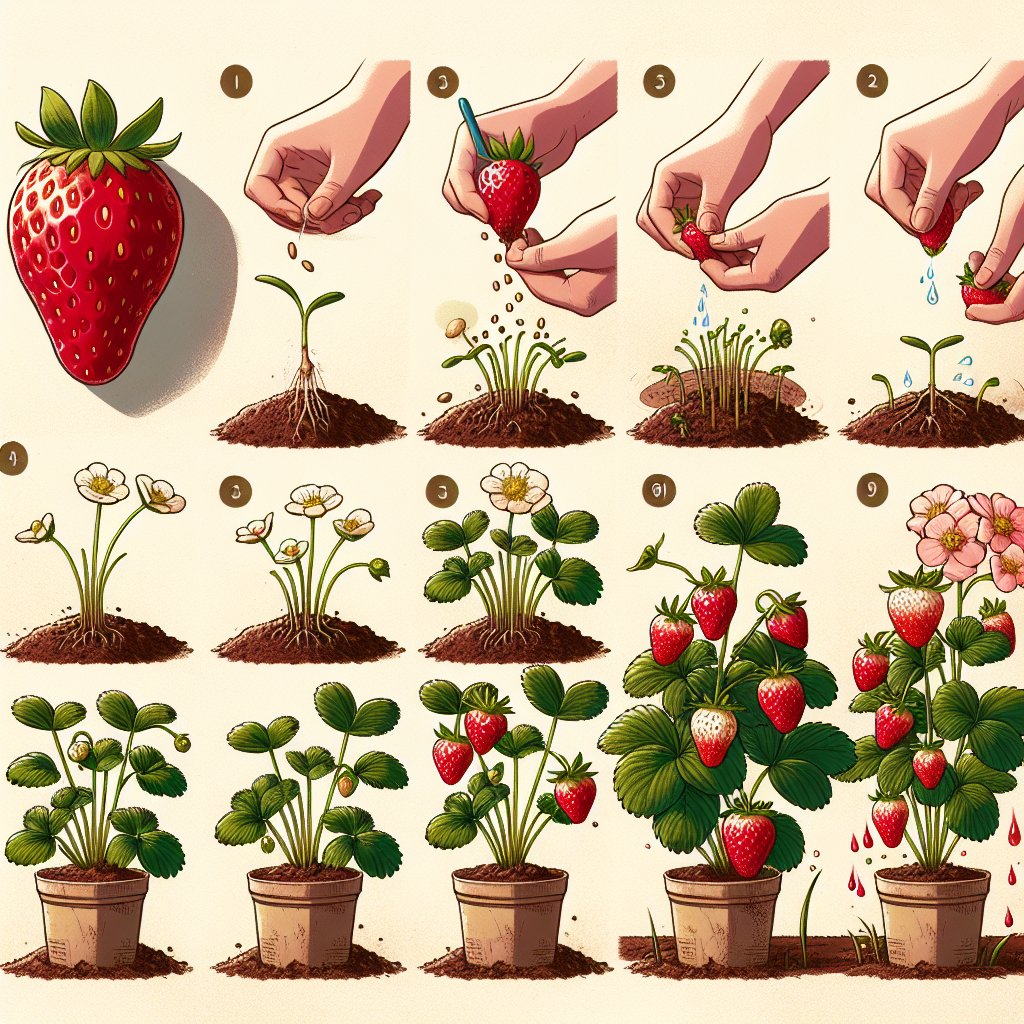
Step-by-Step Process on How to Grow Strawberries from a Strawberry
Follow these steps for a seamless experience in growing strawberries directly from a ripe strawberry:
- Choose the Right Strawberry:
- Extract the Seeds:
- Prepare the Seeds:
- Plant the Seeds:
- Water the Soil:
- Provide Ideal Conditions:
- Remove the Cover:
- Transplanting:
Select an organic, ripe strawberry that is free from blemishes and imperfections. The best results come from juicy, fresh strawberries rather than those that have been in cold storage.
Each strawberry has hundreds of tiny seeds on its surface. Using a knife, carefully cut the strawberry to expose the seeds. You can scrape the seeds off, or you may prefer to blend the strawberry with a bit of water and then strain the mixture through a fine sieve.
Allow the extracted seeds to dry for a day or two. This reduces mold and improves your chances of successful germination.
Fill a container with potting soil or seed starting mix. Scatter the strawberry seeds across the top, ensuring they have enough space between them. Lightly cover them with a thin layer of soil, as they need light to germinate.
Gently mist the soil with a spray bottle to keep it moist but not soaked. Cover the container with plastic wrap or a clear plastic bag to create a greenhouse effect that helps with germination.
Place the container in a warm, well-lit area but avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the seeds. A window sill that receives filtered light will work well.
After about 1-2 weeks, the seeds should start to sprout. Once the seedlings have developed their first true leaves, remove the plastic cover.
When seedlings grow tall enough, they can be transplanted into larger pots or directly into your garden. Be sure to harden them off by exposing them to outdoor conditions gradually over a week.
Caring for Your Strawberry Plants
Once you've successfully transplanted your strawberry plants, it’s essential to provide proper care to ensure they thrive:
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during dry spells. Avoid overwatering, as strawberries do not like soggy roots.
- Fertilizing: Use a balanced fertilizer or compost to ensure your strawberry plants have all the necessary nutrients.
- Mulching: Adding mulch can help retain soil moisture and suppress weeds.
- Pest Control: Keep an eye out for pests such as aphids and spider mites. Organic pesticides can effectively manage these problem areas.
Harvesting Strawberries
After diligent care, you can expect to see your hard work paying off! Here’s how to know when to harvest:
- The strawberries should be fully red, without any green or white patches.
- Pick them in the morning for the best flavor and maintain the freshness.
- Use scissors or shears to cut the berry from the stem, leaving a little bit of the green cap on top.
Common Problems and Solutions When Growing Strawberries
Even with the best intentions, you might run into some issues while growing strawberries. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Yellowing Leaves | Overwatering or nutrient deficiency | Reduce watering and fertilize appropriately |
| Mold On Strawberries | Excess humidity | Improve air circulation and avoid overhead watering |
| Small or Flavorless Berries | Improper watering or insufficient sunlight | Ensure consistent watering and adequate light exposure |
When to Expect Fruit
A good rule of thumb is that strawberry plants will yield fruit within the first year of planting, especially if you started from seeds. However, you should expect a better yield in subsequent years. By keeping the plants healthy and managing their care, you could enjoy strawberries for several years.
Summing Up
Growing strawberries from strawberries is not just a fascinating process; it's a journey that culminates in delicious fruits you can enjoy with friends and family. By following the steps detailed in this guide, you will be well-equipped to start your own strawberry plants, care for them, and eventually harvest the fruits of your labor. Remember, patience is key, and with time and care, you'll be able to indulge in home-grown strawberries. Happy gardening!
By Guest, Published on October 16th, 2024