How to grow tomatoes from fresh tomatoes
How to Grow Tomatoes from Fresh Tomatoes: A Comprehensive Guide
Tomatoes are one of the most popular and versatile vegetables grown in home gardens. Whether you enjoy them fresh in salads, cooked in sauces, or as a base for a myriad of dishes, knowing how to grow tomatoes from fresh tomatoes can lead to rewarding harvests. This guide will take you through the step-by-step process of transforming a fresh tomato into a thriving new plant.
Understanding the Basics of Tomato Seeds
Before diving into the process, it's important to understand that tomatoes can be grown from seeds. When we talk about how to grow tomatoes from fresh tomatoes, we refer to using the seeds contained within ripe tomatoes. Each tomato holds numerous seeds that, if planted correctly, can lead to new tomato plants.
Choosing the Right Tomatoes
Not all tomatoes are equal when it comes to seed viability. Here are some tips for choosing the best tomatoes for seed saving:
- Ripe and Fresh: Select tomatoes that are fully ripe. They should be slightly soft to the touch and free from blemishes.
- Heirloom Varieties: If you're looking for reliable results, heirloom tomatoes are often the best choice as they produce seeds true to type.
- Open-Pollinated Varieties: Avoid hybrid varieties if you plan to save seeds, as they may not produce plants like the original.
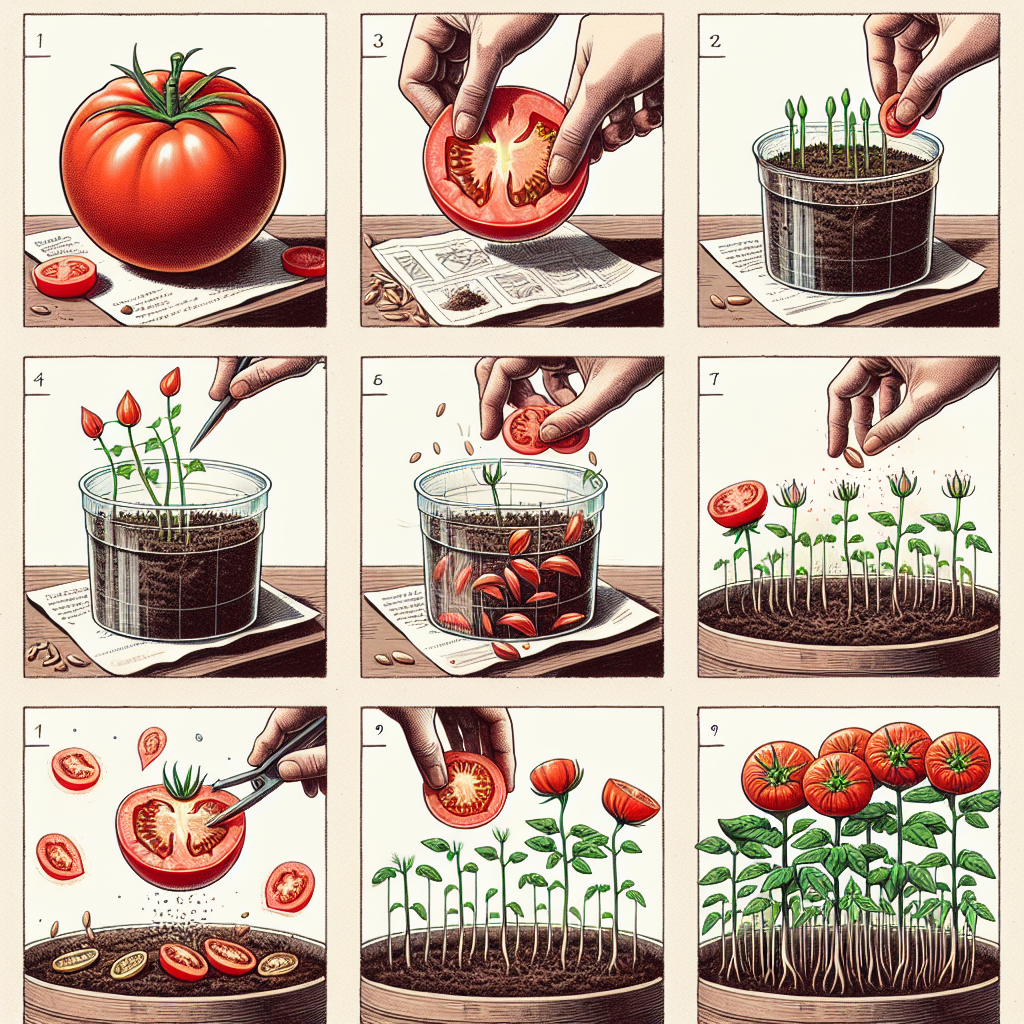
Harvesting Tomato Seeds
Once you've selected your tomatoes, it's time to harvest the seeds:
- Cut the tomato in half horizontally.
- Scoop out the seeds and gel (the surrounding jelly-like substance) into a container.
- Fill the container with water and let it sit for 2-3 days. This fermentation process helps to separate the seeds from the gel.
- After fermentation, pour off the water and any floating debris to separate the seeds. Rinse the seeds under running water.
- Lay the seeds on a paper towel to dry completely before storing.
Preparing for Planting
After you've harvested and dried your seeds, you can start preparing for planting. Timing is crucial for successful tomato growth:
- Start Indoors: In most regions, it's best to start tomato seeds indoors about 6-8 weeks before the last expected frost date.
- Use Seed-Starting Mix: A well-draining seed-starting mix will provide the ideal environment for germination.
- Containers: Use seed trays, peat pots, or recycled containers with drainage holes.
Planting the Seeds
Once you have your containers ready, it’s time to plant:
- Sow the seeds about ¼ inch deep in the prepared soil. Cover them lightly with soil.
- Water gently but thoroughly to moisten the soil.
- Cover the containers with a plastic wrap or a humidity dome to retain moisture until germination.
Providing Ideal Growing Conditions
To ensure successful germination and healthy seedling growth, follow these guidelines:
- Temperature: Keep the soil temperature between 70-75°F (21-24°C) for optimal germination.
- Light: Once seedlings emerge, provide them with at least 12-16 hours of light daily, either from a sunny window or grow lights.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Use a spray bottle for gentle watering.
Transplanting Seedlings
As your seedlings grow and develop two sets of true leaves, they will be ready for transplanting. Here’s what to do:
- Thin out the weaker seedlings, leaving only the strongest one per container.
- Harden off the seedlings by gradually introducing them to outdoor conditions over a week. Start with a few hours a day in a sheltered spot, gradually increasing exposure to sun and wind.
- Transplant the seedlings into larger pots or directly into your garden once temperatures remain consistently warm.
Planting in the Garden
When you're ready to plant in the garden, follow these steps:
- Choose the Right Location: Select an area with full sun, ideally receiving at least 6-8 hours of sunlight daily.
- Soil Preparation: Amend garden soil with compost or well-rotted manure to improve drainage and nutrient content.
- Spacing: Space plants 18-24 inches apart to allow for airflow and growth.
Watering and Care
Watering is a key aspect of tomato care. Here are essential tips:
- Water deeply at the base of the plants to encourage deep root growth.
- Avoid overhead watering to reduce the risk of fungal diseases.
- Mulch around the plants to retain soil moisture and suppress weeds.
Supporting Your Tomato Plants
As they grow, tomato plants will need support to keep their stems sturdy and fruit off the ground. Options for supporting plants include:
- Cages: Tomato cages are widely available and ideal for indeterminate varieties.
- Stakes: Use stakes to support the plants by tying them securely at intervals.
- Trellises: A trellis system can also help maximize space in your garden.
Pest and Disease Management
Keeping your tomato plants healthy involves being aware of common pests and diseases:
- Pests: Watch for aphids, tomato hornworms, and whiteflies. Hand-picking or using insecticidal soap can help manage infestations.
- Diseases: Look for symptoms of blight or blossom-end rot. Ensure good air circulation and avoid overwatering to prevent these issues.
Harvesting Tomatoes
Knowing when to harvest is crucial for enjoying the best tomatoes. Here are some harvesting tips:
- Wait until tomatoes are fully colored and slightly soft to the touch.
- Use scissors or pruning shears to cut the fruit off the vine, leaving a small stem attached to prevent bruising.
- Harvest regularly to encourage continued fruit production.
Conclusion
By following these detailed steps on how to grow tomatoes from fresh tomatoes, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious and home-grown tomatoes. With a bit of patience and care, you can transform your kitchen scraps into thriving tomato plants that will yield fresh produce throughout the growing season. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced gardener, the joy of growing your own tomatoes is an experience worth pursuing.
```By Guest, Published on September 24th, 2024