How to root a fig tree
How to Successfully Root a Fig Tree: A Comprehensive Guide
Rooting a fig tree can be a rewarding experience for any gardener. Fig trees (Ficus carica) are beloved for their sweet fruits and unique leaves. However, many people wonder how to root a fig tree effectively. This article will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to propagate this beautiful plant, tips for success, and FAQs to help you along the way.
Understanding Fig Trees
Before diving into the rooting process, it's essential to understand the characteristics and requirements of fig trees. Fig trees are deciduous plants that thrive in warm climates. They can grow anywhere from 10 to 30 feet tall, depending on the variety and growing conditions. Their roots are robust and sprawling, capable of spreading wide in search of nutrients and water.
- Climate: Fig trees prefer warm, temperate climates but can also tolerate cooler conditions if protected adequately.
- Soil: They thrive in well-draining soil rich in organic matter.
- Water: Regular watering is crucial, especially during dry spells.
Choosing the Right Fig Tree Cutting
The success of rooting a fig tree largely depends on the quality of the cutting you select. Here are some guidelines for choosing the best cutting:
- Select a healthy branch that is at least 6 to 12 inches long.
- Look for a branch that has several nodes (the bumps on the stem), as these will be vital for root development.
- Avoid cuts that are too young or too woody; the ideal cutting is semi-hardwood.
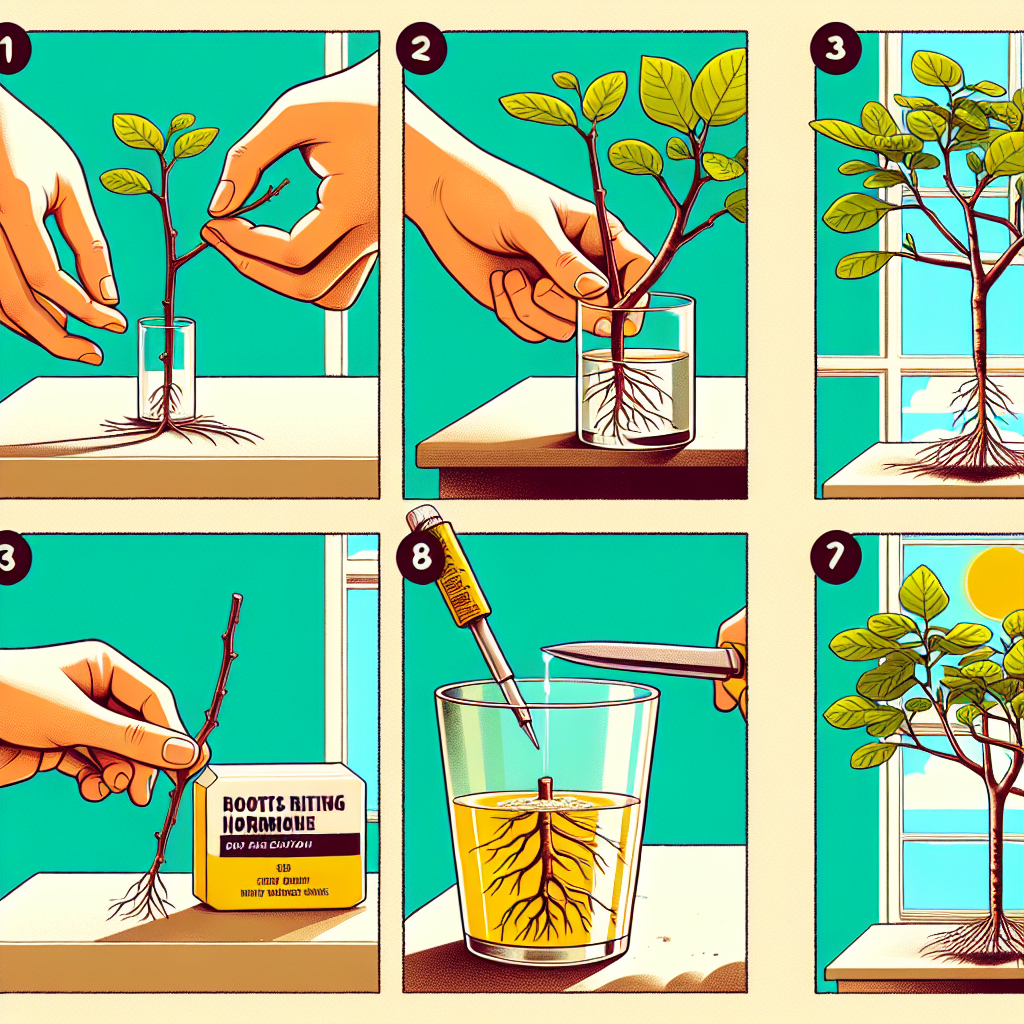
Preparing the Cutting
Once you have chosen your cutting, it's time to prepare it for rooting. Follow these steps:
- Cut below a node using sharp, clean pruning shears. An angled cut is recommended for better surface area.
- Remove any leaves other than the top two, as excess foliage can lead to water loss.
- Dip the cut end in rooting hormone. This step enhances the chances of successful rooting.
Choosing the Best Medium for Rooting
Rooting hormones and selecting a proper medium are crucial for success. Here are your options:
- Coconut Coir: This natural material retains moisture and allows for good aeration.
- Pine Bark: This provides good drainage while retaining some moisture.
- Perlite and Vermiculite Mix: This combination promotes healthy root growth.
Planting Your Fig Tree Cutting
Now that your cutting is prepared, you can plant it. Follow these steps:
- Fill a small pot or container with your chosen medium and water it to ensure it is moist, but not soggy.
- Make a hole in the medium with your finger or a pencil. This will prevent damaging the cutting when you insert it.
- Place the cutting into the hole, ensuring that at least one node is buried in the medium.
- Gently press the medium around the base of the cutting to hold it in place.
- Water lightly once more to settle the medium around the cutting.
Caring for Your Fig Tree Cutting
After planting, providing proper care is essential for the rooting process:
- Humidity: Fig cuttings thrive in high humidity. Cover the pot with a plastic bag or use a humidity dome to create a greenhouse effect.
- Temperature: Keep the cutting in a warm, bright area with indirect sunlight.
- Watering: Check the medium regularly and water lightly when it feels dry. Avoid overwatering.
Monitoring Root Development
It’s vital to monitor your cutting for signs of root development, which typically takes several weeks:
- Check for new growth, which indicates that the cutting is establishing roots.
- Gently tug on the cutting after a few weeks to see if there is resistance. If you feel resistance, roots are probably forming.
- Roots will generally develop within 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the conditions.
Transplanting Your Rooted Fig Cutting
Once your fig tree cutting has developed sufficient roots, it’s time to transplant it to a larger container or directly into the garden:
- Choose a new pot that is at least 8-10 inches wide with drainage holes.
- Fill the pot with high-quality potting soil.
- Carefully remove the rooted cutting from its original pot, being cautious to minimize stress on the roots.
- Plant the cutting in the new pot, filling in with soil around the base and pressing gently to secure it.
- Water thoroughly to help settle the soil around the new roots.
Final Tips for Success
Rooting a fig tree can sometimes be a hit-or-miss process, but here are some additional tips to increase your chances of success:
- Timing: The best time to take cuttings is late spring or early summer when the tree is actively growing.
- Patience: If rooting takes longer than expected, resist the temptation to dig up the cutting too early.
- Research: Look into specific fig tree varieties to tailor your approach based on their unique needs.
Dealing with Common Issues
Like any gardening activity, rooting fig trees can present challenges. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Mold: If you notice mold on the cutting or medium, reduce humidity slightly and ensure proper air circulation.
- Leaf Drop: This can occur due to stress; if leaves are dropping, check environmental factors, like temperature and moisture.
- Wilting: If the cutting wilts despite moisture, it may have rotted. Ensure the medium drains well, and adjust watering accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rooting a fig tree can be a fulfilling endeavor that rewards you with a beautiful plant and the promise of delicious fruits. By following the above steps on how to root a fig tree and being attentive to your cutting's needs, you’ll set yourself up for success. Happy gardening!
By Guest, Published on September 23rd, 2024