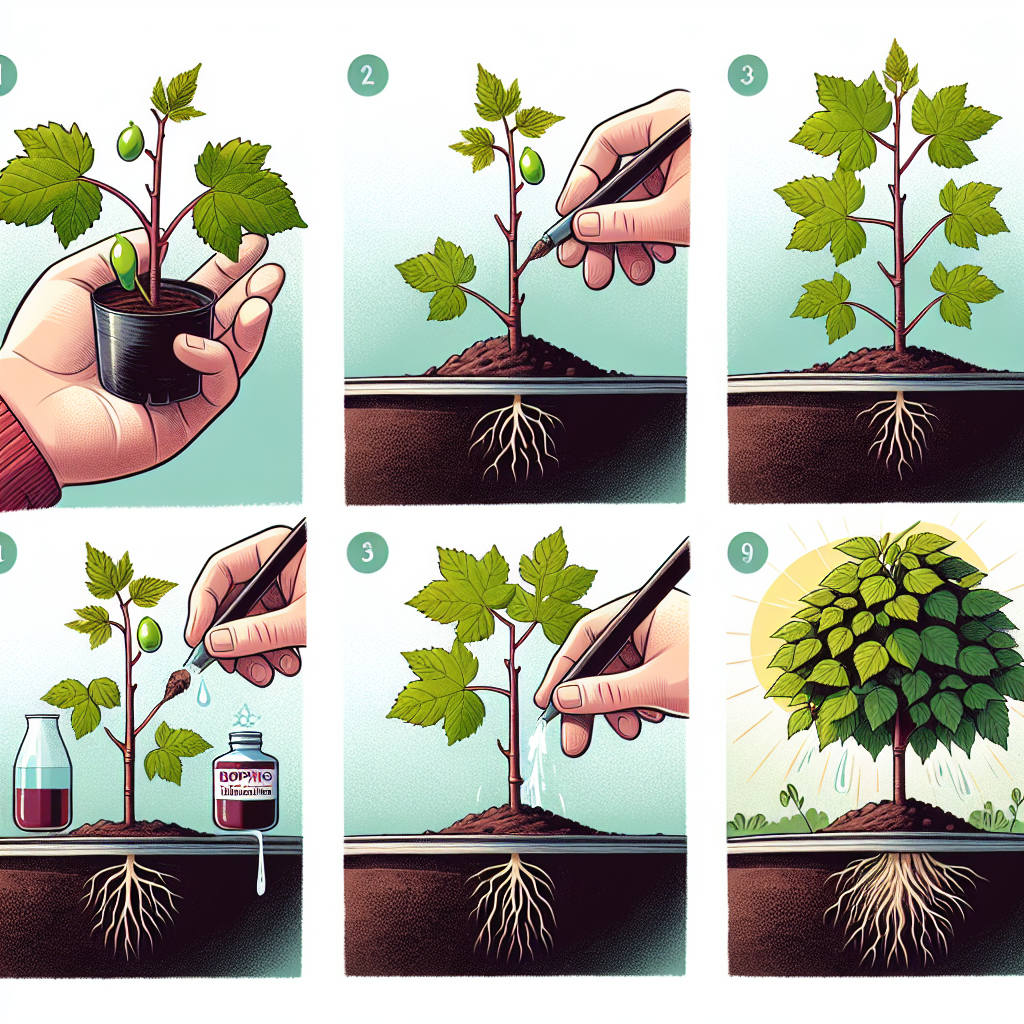
How to start new grape vines from cuttings
How to Start New Grape Vines from Cuttings: A Comprehensive Guide
Grapes are one of the oldest cultivated fruits in the world, enjoyed for their sweetness and versatility. If you're a gardening enthusiast or looking to establish your own vineyard, learning how to start new grape vines from cuttings can be a rewarding and cost-effective venture. Cuttings allow you to propagate your favorite grape varieties without the need for expensive seedlings or purchasing entire plants. In this guide, we will take you through the entire process from selecting the right cuttings to caring for your new vines.
Understanding Grape Vines and Their Varieties
Before delving into the propagation process, it’s essential to understand the different types of grape vines. There are primarily two categories: table grapes and wine grapes. Each type has various cultivars, each with unique characteristics. Here’s a brief overview:
- Table Grapes: These varieties are typically sweeter and are enjoyed fresh. Examples include Thompson Seedless and Concord.
- Wine Grapes: These are generally smaller and have more concentrated flavors, essential for winemaking. Varieties include Cabernet Sauvignon and Chardonnay.
For propagation, consider the grape variety you would like to grow and ensure it is suited for your climate and soil type.
The Best Time for Taking Cuttings
The right timing can significantly influence the success rate of your propagation efforts. The optimal time to take grape vine cuttings is during late winter or early spring, just before new growth begins. This period allows the cuttings to establish roots before the growing season kicks in.
How to Select Healthy Cuttings
The key to successful propagation lies in selecting healthy cuttings. Here are some tips:
- Choose a vigorous vine: Look for a grapevine that is healthy and free from pests or diseases.
- Opt for one-year-old wood: Ideal cuttings should come from one-year-old stems, as they have the best chance of rooting.
- Avoid year-old canes: These may not root as effectively as younger wood.
Take cuttings that are about 6-8 inches long, with 2-3 nodes (the bumps on the stem) present. This increases the likelihood of successful rooting.
Preparing Cuttings for Planting
Once you have your cuttings ready, the next step is preparation. Follow these guidelines:
- Make a clean cut: Use a sharp, sterilized knife to ensure clean cuts and reduce the risk of disease.
- Trim the leaves: Remove any leaves on the lower half of the cutting, as they can rot when planted.
- Make a cut at the bottom: Create a diagonal cut just below the bottom node to enhance water intake.
- Optional: Use rooting hormone: While not strictly necessary, applying a rooting hormone can improve your chances of success.
Choosing the Right Planting Medium
The success of your cuttings also depends on the quality of the planting medium. A good mix promotes drainage while retaining moisture. Consider the following options:
- Perlite: This lightweight material provides excellent drainage.
- Vermiculite: Retains moisture while still allowing for air circulation.
- Pine bark: Offers a natural medium that drains excess water while retaining some moisture.
A combination of these materials can provide the ideal conditions for rooting your cuttings.
Planting Your Cuttings
With your cuttings prepped and your medium ready, it’s time to plant. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Fill a pot or container with the planting medium, leaving about an inch from the top.
- Moisten the medium lightly to ensure it is damp but not soaking wet.
- Make a small hole in the center with your finger or a pencil to accommodate the cutting.
- Insert the cutting into the hole, ensuring that at least one node is buried in the medium.
- Firm the medium around the cutting gently and water it again to settle the soil.
Creating the Ideal Environment
Once planted, your cuttings will need a conducive environment to encourage rooting. Here are some tips to create an ideal setting:
- Humidity: High humidity is crucial for rooting. Cover the pot with a plastic bag or place it in a mini-greenhouse setup to retain moisture.
- Light: Provide bright, indirect light but avoid direct sunlight, which can overheat the cuttings.
- Temperature: Maintain a stable temperature of 65-75°F (18-24°C) for optimal growth.
Watering and Maintenance
Monitoring moisture levels is critical during the rooting phase. Here are a few maintenance tips:
- Check the moisture levels daily; the medium should remain moist but not soggy.
- Remove the plastic covering for a few hours each day to allow for air circulation and prevent mold.
- Look for signs of growth: In 4-6 weeks, you should notice new growth, indicating successful rooting.
Transplanting Your New Vines
Once your cuttings have rooted and show signs of growth, it’s time to transplant them into larger pots or into the garden. Here’s how to do it:
- Choose a sunny location in your garden with well-drained soil.
- Prepare the planting hole, ensuring it is deep and wide enough for the root system.
- Carefully remove the rooted cutting from its pot, taking care not to damage the roots.
- Place the vine into the hole and fill it with soil, gently pressing down to eliminate air pockets.
- Water thoroughly to help settle the soil around the roots.
Care for Your Young Grape Vines
After transplanting, it’s essential to continue caring for your young grape vines. Follow these guidelines:
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially in the first growing season.
- Fertilization: Use a balanced fertilizer every few weeks during the growing season.
- Pruning: As your vines grow, prune unnecessary shoots to encourage healthy growth.
Potential Issues to Watch Out For
Like any plant, young grape vines can be susceptible to diseases and pests. Here’s what to look out for:
- Powdery Mildew: This fungal disease manifests as white powder on leaves. Prevent it by ensuring proper air circulation.
- Root Rot: Overwatering can lead to root rot; ensure proper drainage in the planting medium.
- Pests: Keep an eye out for aphids and spider mites; if found, treat with insecticidal soap.
Conclusion: Enjoying the Fruits of Your Labor
Learning how to start new grape vines from cuttings is not only a practical skill for gardening enthusiasts but also a fulfilling endeavor that can yield delicious fruits for years to come. With the right care and techniques, you’ll soon have healthy grapevines laden with fruit, ready for harvesting. Whether for fresh consumption, winemaking, or simply to enhance your garden, grapevines can be an excellent addition to your horticultural pursuits.
Now that you’re equipped with the knowledge to propagate grape vines from cuttings, why not give it a try? Embrace the art of growing your vines and enjoy the bountiful rewards they bring!
By Guest, Published on September 15th, 2024